
Government injects income back into the economy by spending (G) on public and merit goods like defence and policing, education, and healthcare, and also on support for the poor and those unable to work.įinally, the model must be adjusted to include international trade.
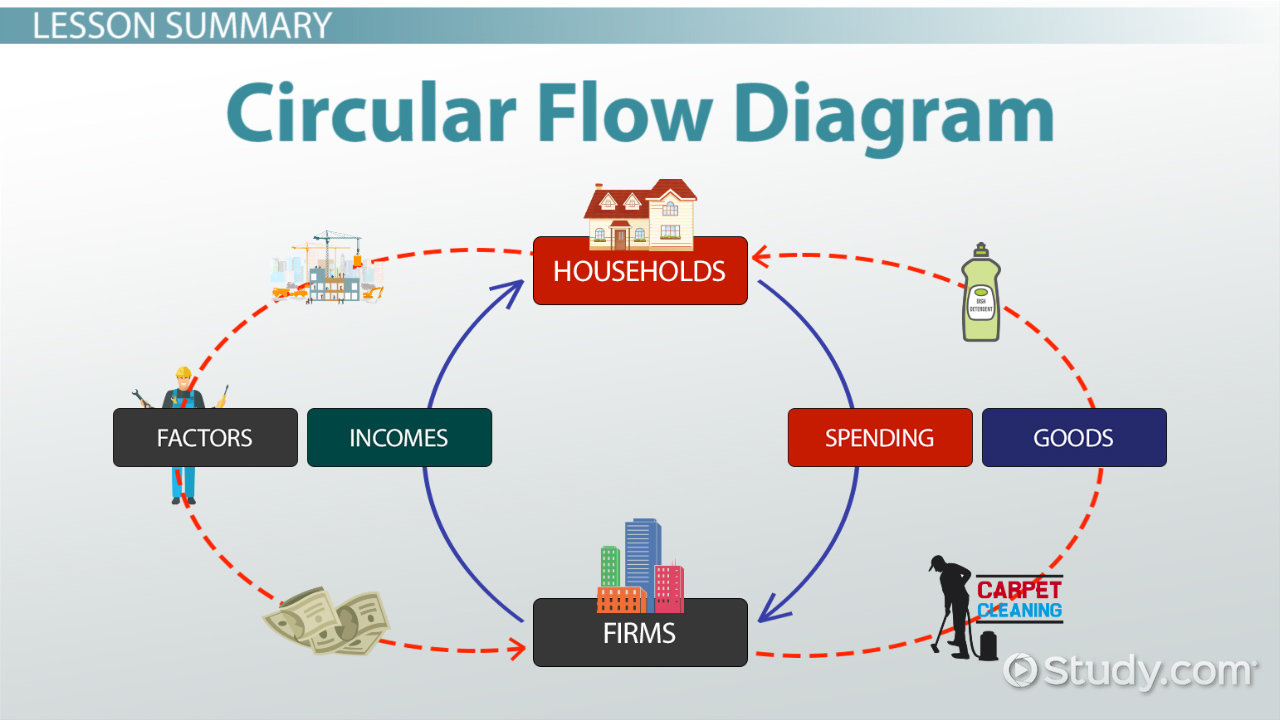
Therefore, as well as save, households are also likely to pay taxes (T) to the government (G), and further income is withdrawn out of the circular flow of income. In a mixed economy with a government, the simple model must be adjusted to include the public sector. This process, called investment (I), occurs because existing machinery wears out and because firms may wish to increase their capacity to produce. However, firms also purchase capital goods, such as machinery, from other firms, and this spending is an injection into the circular flow. Marginal decisions to save reduce the flow of income in the economy because saving is a withdrawal out of the circular flow. Households may choose to save (S) some of their income (Y) rather than spend it (C), and this reduces the circular flow of income. The simple circular flow is, therefore, adjusted to take into account withdrawals and injections. A net injection relates to the overall effect of injections in relation to withdrawals following a change in an economic variable. An injection of new spending will increase the flow. The circular flow will adjust following new injections into it or new withdrawals (aka leakages) from it.

The circular flow of income forms the basis for all models of the macro-economy, and understanding the circular flow process is key to explaining how national income, output and expenditure is created over time. Spending and income continue to circulate around the macro economy in what is referred to as the circular flow of income. New spending (C) generates new income (Y), which generates further new spending (C), and further new income (Y), and so on. Income (Y) in an economy flows from one part to another whenever a transaction takes place. Q = f (L, La, K) The Circular flow of income The simple production function states that output (Q) is a function (f) of: (is determined by) the factor inputs, land (L), labour (La), and capital (K), i.e. Members of households pay for goods and services they consume with the income they receive from selling their factor in the relevant market. Land receives rent, human capital receives a wage, real capital receives a rate of return, and enterprise receives a profit. Factor incomesįactors of production earn an income which contributes to national income. To do this they use factors and pay for their services. The function of firms is to supply private goods and services to domestic households and firms, and to households and firms abroad. Entrepreneurs combine the other three factors, and bear the risks associated with production.

L and is supplied by landowners, human capital by labour, real c apital by capital owners (capitalists) and e nterprise is provided by entrepreneurs. The factors are supplied by factor owners in return for a reward. The primary economic function of households is to supply domestic firms with needed factors of production – land, human capital, real capital and enterprise.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
